HOME › 各部案内 › 創薬基盤研究部 › 細胞核輸送ダイナミクスプロジェクト(共同研究者 米田 悦啓)


米田 悦啓 Yoshihiro Yoneda, M. D., Ph. D国立研究開発法人 医薬基盤・健康・栄養研究所研究所長
研究内容
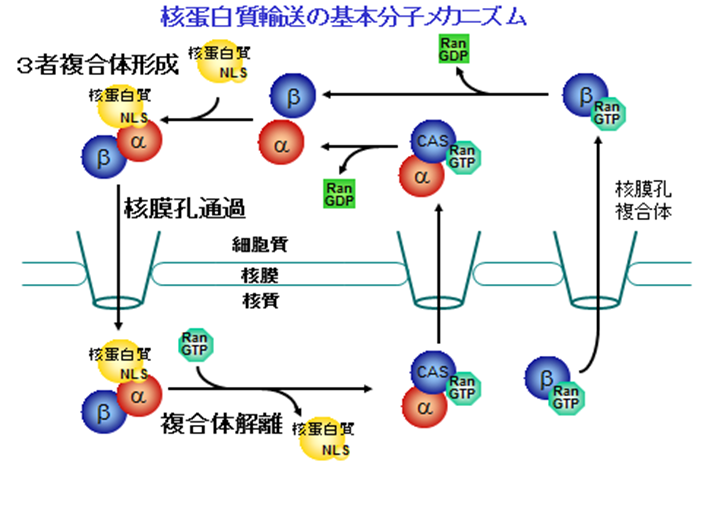
「核輸送制御と高次生命現象」
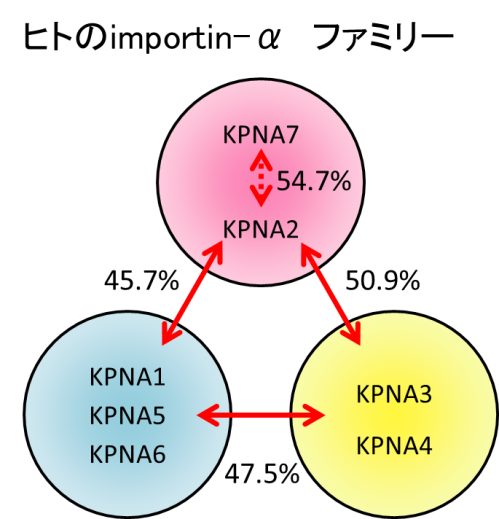
高等真核生物においては、輸送因子であるimportinやexportin、あるいは核膜孔の多様化が見られることが知られている。例えば、核移行シグナル(NLS)受容体であるimportin-αは出芽酵母では1種類しか存在しないのに対し、哺乳類では複数種存在して大きなファミリーを形成していることが分かっている。
そして、それらによる組織・発生時期特異的なタンパク質輸送制御は高次生命現象の様々な場面に深く関わっている。このような輸送制御機構の分子基盤を明らかにする目的で、発生、細胞分化時におけるタンパク質輸送制御機構、およびがんをはじめとする病態におけるタンパク質輸送異常を中心に研究を進めている。
「核輸送ネットワークとクロマチン相互作用」
近年、核輸送因子や核膜孔の構成因子(ヌクレオポリン)が輸送に関連して働くだけではなく、核内でクロマチンと物理的・機能的な相互作用を示す事が明らかになってきた。これらの核輸送関連因子ネットワークとクロマチンの相互作用に関して同様に研究を進めている。
【参考文献】
1) Yasuhara, N., Yamagishi, R., Arai, Y., Mehmood, R., Kimoto, C., Fujita, T., Touma, K., Kaneko, K., Kamikawa, Y., Moriyama, Y., Yanagida, T., Kaneko, H. and Yoneda, Y. Importin alpha subtypes determine differential transcription factor localization in embryonic stem cells maintenance. Dev. Cell, 26: 123-135 (2013)
2) Morita, M., Kuba, K., Ichikawa, A., Nakayama, M., Katahira, J., Iwamoto, R., Watanabe, T., Sakabe, S., Daidoji, T., Nakamura, S., Kadowaki, A., Ohto, T., Nakanishi, H., Taguchi, R., Nakaya, T., Murakami, M., Yoneda, Y., Arai, H., Kawaoka, Y., Penniger, J. M., Arita, M. and Imai, Y. The lipid mediator protectin D1 inhibits influenza virus replication and improves severe influenza. Cell, 153: 112-125 (2013)
3) Kressler, D., Bange, G., Ogawa, Y., Stjepanovie, G., Bradatsch, B., Pratte, D., Amlacher, S., Straus, D., Yoneda, Y., Katahira, J., Sinning, I. and Hurt, E. Synchronizing nuclear import of ribosomal proteins with ribosome assembly. Science, 338: 666-671 (2012)
4) Yasuda, Y., Miyamoto, Y., Yamashiro, T., Asally, M., Masui, A., Loveland, K.L. and Yoneda, Y. Nuclear retention of importin coordinates cell fate through changes in gene expression. EMBO J.,31: 83-94 (2011)
5) Okada, C., Yamashita, E., Lee, S. J., Shibata, S., Katahira, J., Nakagawa, A., Yoneda, Y. and Tsukihara, T. A high-resolution structure of the pre-microRNA nuclear export machinery. Science, 326: 1275-1279 (2009)
6) Otsuka, S., Iwasaka, S., Yoneda, Y., Takeyasu, K. and Yoshimura, S. H. Individual binding pockets of importin for FG-nucleoporins are differently regulated by RanGTP. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 105: 16101-16106 (2008)
7) Bradatsch, B., Katahira, J., Kowalinski, E., Bange, G., Yao, W., Sekimoto, T., Baumgärtel, V., Boese, G., Bassler, J., Wild, K., Peters, R., Yoneda, Y., Sinning, I. and Hurt, E. Arx1 functions as an unorthodox nuclear export receptor for the 60S pre-ribosomal subunit. Mol. Cell, 27: 767-779 (2007)
8) Yasuhara, N., Shibazaki, N., Tanaka, S., Nagai, M., Kamikawa, Y., Oe, S., Kamachi, Y., Kondoh, H. and Yoneda, Y. Triggering neural differentiation of ES cells by subtype switching of importin-. Nature Cell Biol., 9: 72-79 (2007)
9) Kotera, I., Sekimoto, T., Miyamoto, Y., Saiwaki, T., Nagoshi, E., Sakagami, H., Kondo, H. and Yoneda, Y. Importin transports Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase type IV (CaMKIV) to the nucleus without utilizing importin . EMBO J., 24: 942-951 (2005)
10) Lee, S. J., Sekimoto, T., Yamashita, E., Nagoshi, E., Nakagawa, A., Imamoto, N., Yoshimura, M., Sakai, H., Chong, K. T., Tsukihara, T. and Yoneda, Y. The structure of importin- bound to SREBP-2: Insights into nuclear import of a transcription factor. Science, 302: 1571-1575 (2003)





